Introduction
GraphQL is a fast and modern way to fetch data to your application. It has many advantages, such as: caching, speed and unified data model. It sits between your backend and frontent:
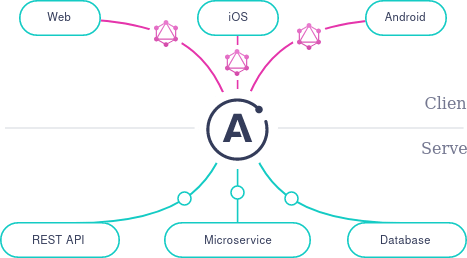 We will be implementing a very simple GraphQL use case for Node.js backend and React.js frontend.
We will be implementing a very simple GraphQL use case for Node.js backend and React.js frontend.
Middleware and Backend
We'll use Apollo and Express server integration: apollo-server-express.
npm i create-react-app graphql apollo-server-express express
Create a folder for a server side:
mkdir server
code apollo_server.js
In the apollo_server.js file import the modules:
const express = require('express');
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server-express');
Then construct a schema with GraphQL language for variables that you will be fetching. Define the type for variables, here it will be a string:
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
user: String,
email: String
}
`;
Now let's create some dummy data. We will later replace this with MongoDB data.
const test_user = 'jaguar'
const test_email = 'jaguar@gmail.com'
Let's use it and create Query resolvers:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user: () => test_user,
email: () => test_email,
},
};
Now let's run Apollo Server and make it a middleware in front of our express server:
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
const app = express();
server.applyMiddleware({ app });
app.listen({ port: 4000 }, () =>
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at http://localhost:4000${server.graphqlPath}`)
);
We can start the server with:
node apollo_server.js
The whole apollo_server.js file should look like this:
const express = require('express');
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server-express');
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
user: String,
email: String
}
`;
const test_user = 'jaguar'
const test_email = 'jaguar@gmail.com'
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user: () => test_user,
email: () => test_email,
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
const app = express();
server.applyMiddleware({ app });
app.listen({ port: 4000 }, () =>
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at http://localhost:4000${server.graphqlPath}`)
);
Now let's move on to the front-end.
Frontend
Let's create the folder and the starting application:
mkdir client
cd client
npm i -g create-react-app
create-react-app test_book
cd test_book
npm i @apollo/react-hooks apollo-boost
cd src
code index.js
Import the Apollo hooks, client and connect it to the server:
import { ApolloProvider } from '@apollo/client';
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000',
});
Add Apollo Client context to the App component:
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<App />
</ApolloProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
The whole index.js file should look like this:
import { ApolloProvider } from '@apollo/client';
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/graphql',
});
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<App />
</ApolloProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
serviceWorker.unregister();
Now we will use useQuery hook to query data from the Apollo server. Open App.js:
const USER_QUERY = gql`
{
user
email
}
`;
Fetch the data, display whether the data was loading or an error happened:
const App = () => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(USER_QUERY);
if (loading) {
return <p>Loading...</p>;
}
if (error) {
console.log(error)
return <p>Error :(</p>;
}
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<p>
User is: {data.user}
</p>
<p>
Email is: {data.email}
</p>
</header>
</div>
);
}
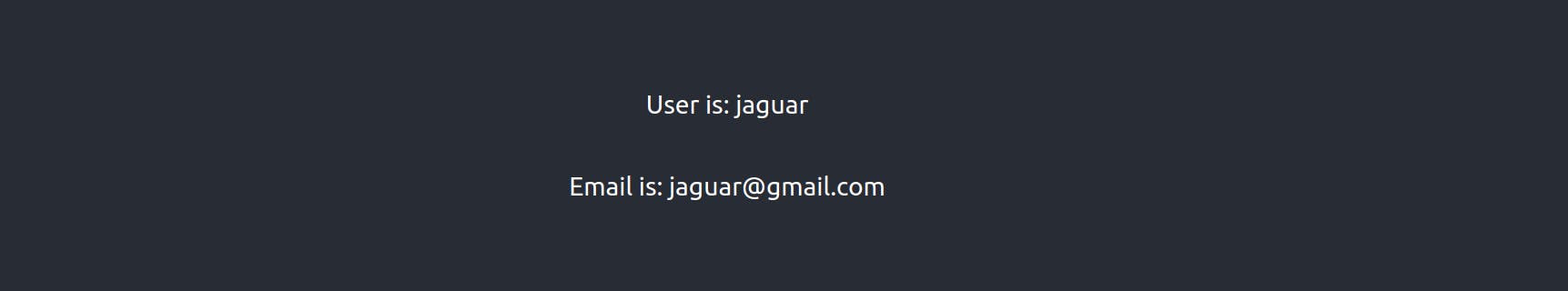
You shoul see the data successfully loaded in the browser:
 The whole App.js file should be:
The whole App.js file should be:
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import { useQuery } from '@apollo/react-hooks';
import { gql } from 'apollo-boost';
const USER_QUERY = gql`
{
user
email
}
`;
const App = () => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(USER_QUERY);
if (loading) {
return <p>Loading...</p>;
}
if (error) {
console.log(error)
return <p>Error :(</p>;
}
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<p>
User is: {data.user}
</p>
<p>
Email is: {data.email}
</p>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Enjoy - you just made a successfull GraphQL query! In the following tutorial we will tailor our query to the full user model.
Let the good times roll!